Introduction to the Rescoring Tool
The Rescoring Tool is designed to enhance molecular docking results, particularly for nucleic acid targets, by integrating advanced deep learning and structural analysis techniques. It refines initial docking poses through sophisticated models to improve binding affinity predictions and generates diverse molecular conformations for better structural sampling.
This tool employs a dual-task transformer model for classification (DNA/RNA) and binding affinity regression, utilizing Graph Attention Networks (GAT) for conformer generation and molecular structure analysis. Furthermore, it extracts geometric, chemical and interaction properties from molecular complexes to inform its predictions and uses RMSD-based pose selection to identify optimal binding poses.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Execute the Tool
This is the Rescoring tool's application workspace page, where various options for predicting binding affinity and generating diverse molecular conformations for better structural sampling are available. This tutorial will explain each option in detail.
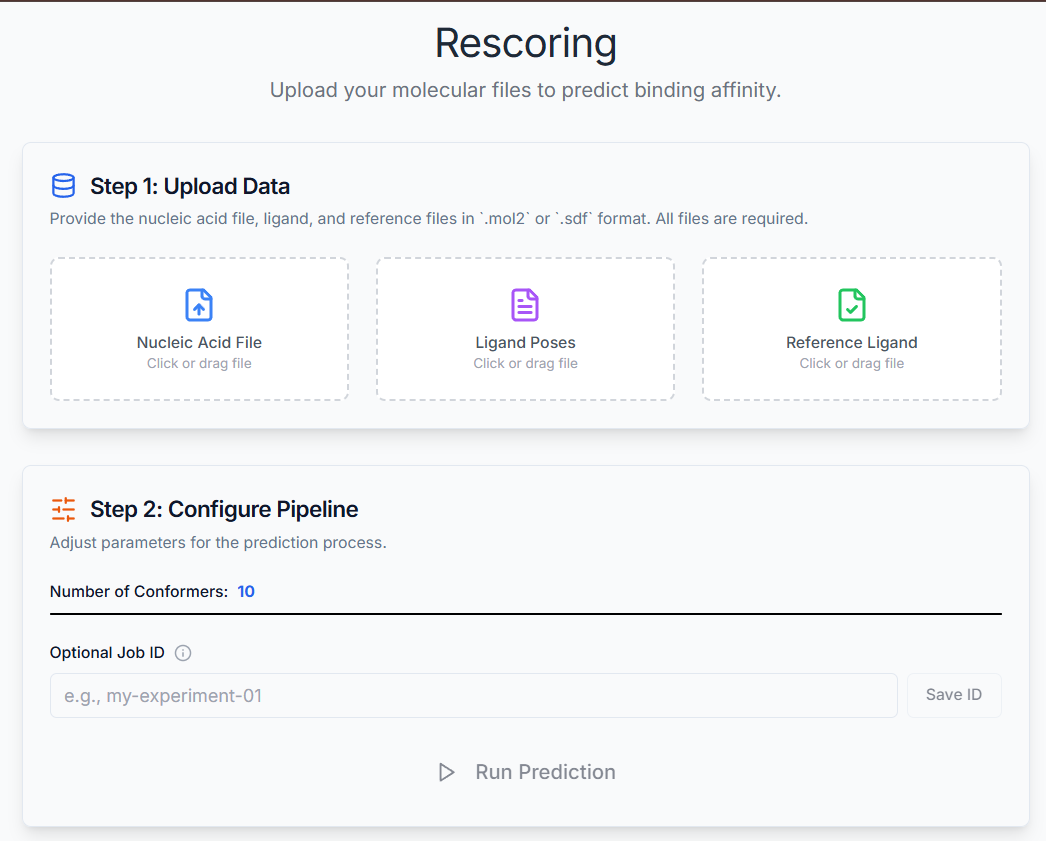
Upload the nucleic acid .mol2 file, ligand poses in .sdf format, and reference ligand in .sdf format.
Configuring and Running the Prediction
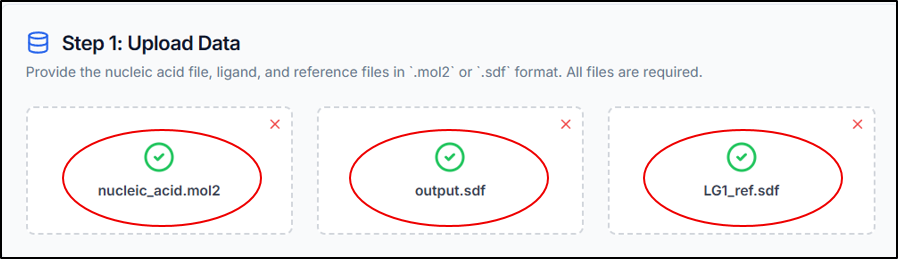
Adjust the slidebar accordingly for the number of conformers to be generated per ligand.
Click on "Run Prediction" to run the Rescoring Tool.

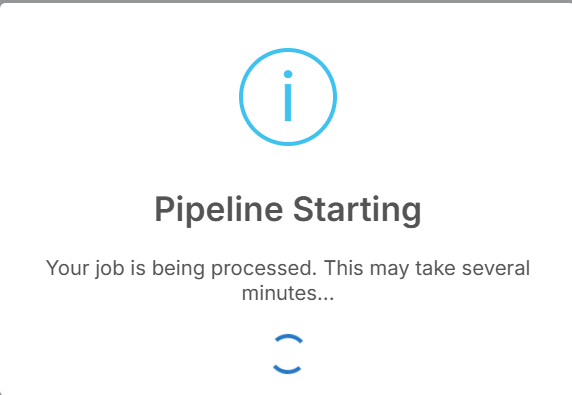
After clicking on "Run Prediction", this pop-up will appear showing that the Rescoring pipeline has been started.
Analyzing the Results
After completion of the rescoring pipeline, the predictions will be displayed below, mentioning the class, class_confidence, complex_name, pose_number, and RMSD values of all the conformers.
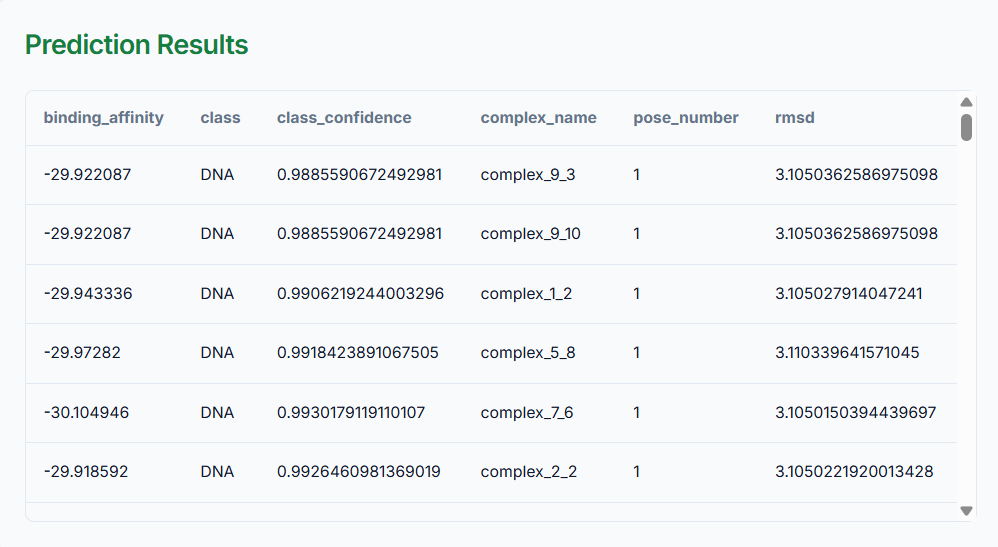
The Rescoring Tool has successfully completed its pipeline execution. This process has demonstrably refined the initial docking results by giving improved binding affinity predictions for the top conformers. These rescored predictions represent a more accurate assessment of ligand-target interaction compared to the original docked ligand by significantly improving the reliability of the findings.
