Introduction to DeNovo-Generator
DeNovo-Generator is an AI-powered computational tool that creates novel molecular structures from scratch, without relying on existing molecule databases. It leverages deep learning architectures to understand chemical space and generate molecules that satisfy specific therapeutic requirements and drug-like properties. This powerful approach enables researchers to discover entirely new chemical scaffolds, bypass the limitations of existing libraries, and accelerate the discovery of promising lead compounds.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Execute the Tool
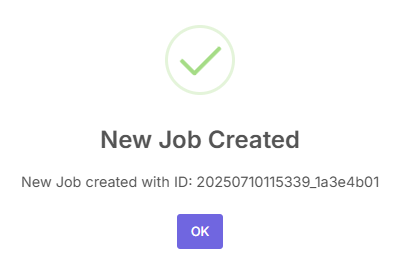
Before starting, you must create a JOB ID. You can enter a custom name or simply click the "Create Job ID" button to have one automatically generated.
TIP: You will not be able to proceed or access any tool features without first creating a JOB ID.
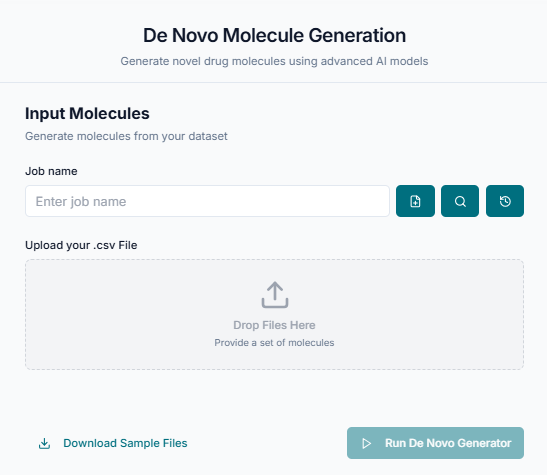
First, you must provide the input for the generation process. Click the "Upload File" button and upload your DeNovo input file. This file must be a .csv file that is structured according to the tool's requirements.
Tip: A sample input file is provided to show you the required format. It is highly recommended to download and review the sample before preparing your own file to ensure a successful run.
Generating and Downloading Molecules
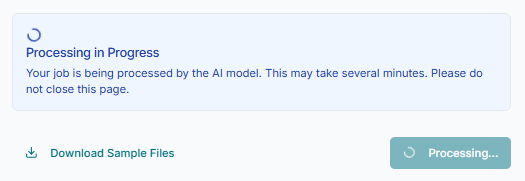
Once your input file is successfully uploaded, the generation process will begin. The screen will show a progress indicator, confirming that the tool is actively working on designing the new molecules based on your input.
Tip: The AI model is now exploring chemical space to design novel structures. This step may take a few moments, so please wait for the process to complete.

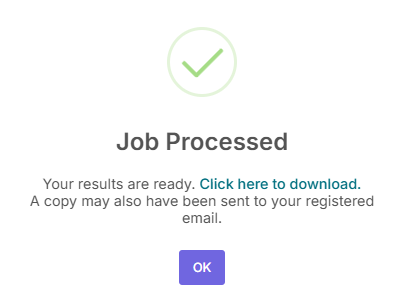
Once the generation is finished, a "Job Processed Successfully" message will appear. The results are now ready for download.
Click the "Download" link or button to save the CSV file containing your newly generated molecules to your computer.
So, by using the DeNovo-Generator tool, you have successfully generated a library of novel molecular structures designed specifically to fit your target's binding site.
