Introduction to Density Functional Theory (DFT)
Density Functional Theory (DFT) is a powerful and highly accurate quantum chemical method used to investigate the electronic structure of molecular systems. In the context of drug discovery, it serves as an important tool for post-docking and post-molecular dynamics analysis.
Instead of solving the complex Schrödinger equation, DFT's core principle is to calculate a system's properties based on its electron density—a much more manageable variable—by solving the Kohn-Sham equations with carefully chosen exchange-correlation functionals and basis sets. This approach yields a wealth of information, including the HOMO-LUMO gap, ionization potential, and electrostatic potential maps, which are essential for characterizing a molecule's chemical reactivity, kinetic stability, and intermolecular interaction profile with high precision.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Execute the Tool
Before executing the tool, you must create a Job ID. You can customize this ID or click the "Create Job ID" (+) button to have one generated for you automatically.
TIP: Without creating a JOB ID, you will not be able to access any options of the tool.

This is the home page of the DFT tool, where you can paste a SMILES string or draw a molecule in the sketcher, fetch it, and predict properties like HOMO-LUMO, Mulliken charges, and ESP.
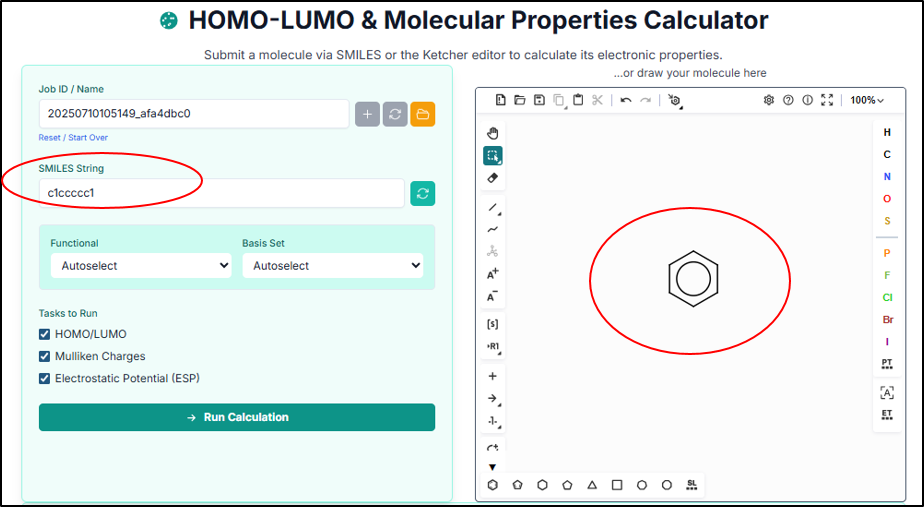
Configuring and Running the Calculation
In this step, select the Functional and Basis Set for the DFT calculation, or leave them on Autoselect for automatic configuration.
Choosing Your Functional and Basis Set
The choice of Functional and Basis Set significantly impacts the accuracy and computational cost of your DFT calculations. Here's a guide to help you select the best options for common scenarios:
| Scenario / Goal | Functional | Basis Set | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| General property prediction | B3LYP | 6-31G(d) | Fast, widely benchmarked, and accurate for geometry, HOMO–LUMO gap, and dipole moment |
| Molecules with F, Cl (halogens) | B3LYP | 6-311+G(d,p) | Improved dipole and orbital accuracy due to diffuse and polarization functions |
| Molecules with S or Br | B3LYP | def2-SVP | Efficient treatment of heavier atoms with relativistic effective core potentials (ECPs) |
| Polar functional groups (OH, NH₂, NO₂) | B3LYP | 6-311+G(d,p) | Better lone-pair description and dipole accuracy for polar substituents |
| Extended π-conjugation / Delocalized orbitals (e.g. stilbene, coumarin, rhodamine dyes) |
B3LYP | def2-TZVP | Provides more accurate orbital energies and delocalization than minimal basis sets |
| If B3LYP fails (poor SCF convergence or inaccurate) | M06-2X or ωB97X-D | def2-SVP or def2-TZVP | Use these for highly delocalized or dispersion-sensitive systems as a fallback |
Select the desired tasks such as HOMO/LUMO, Mulliken Charges, and ESP, and click "Run Calculation" to start the DFT analysis.

Analyzing the Results
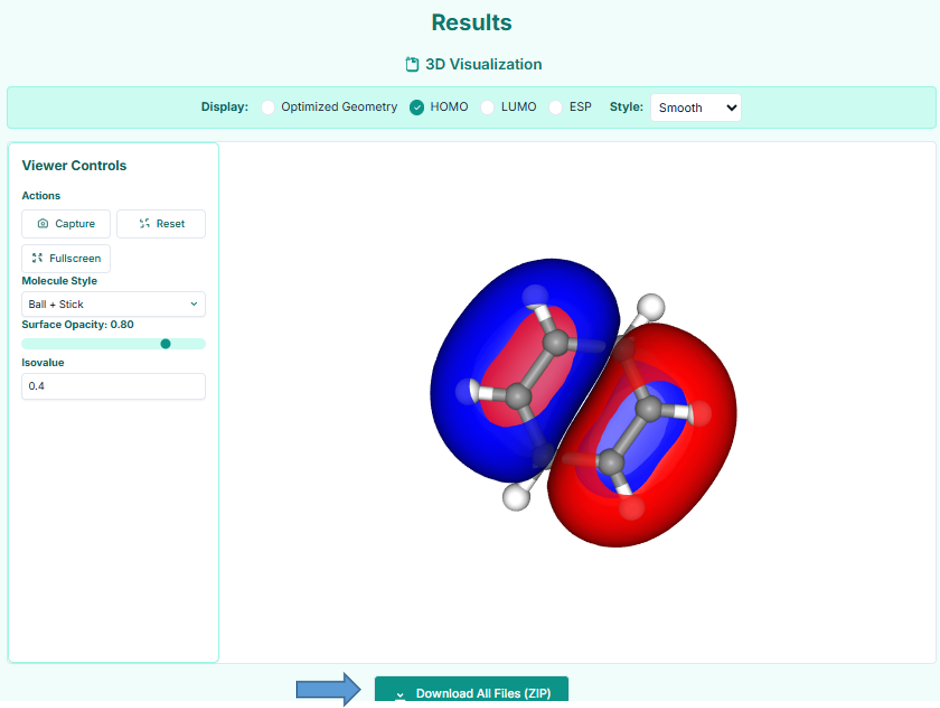
This is the results page where you can visualize the optimized geometry, HOMO, LUMO, or ESP in 3D, adjust display settings, and download all output files.
The DFT tool provides a comprehensive report by tabulating key electronic properties, including HOMO-LUMO energies, reactivity descriptors, and atomic Mulliken charges for a detailed chemical analysis.
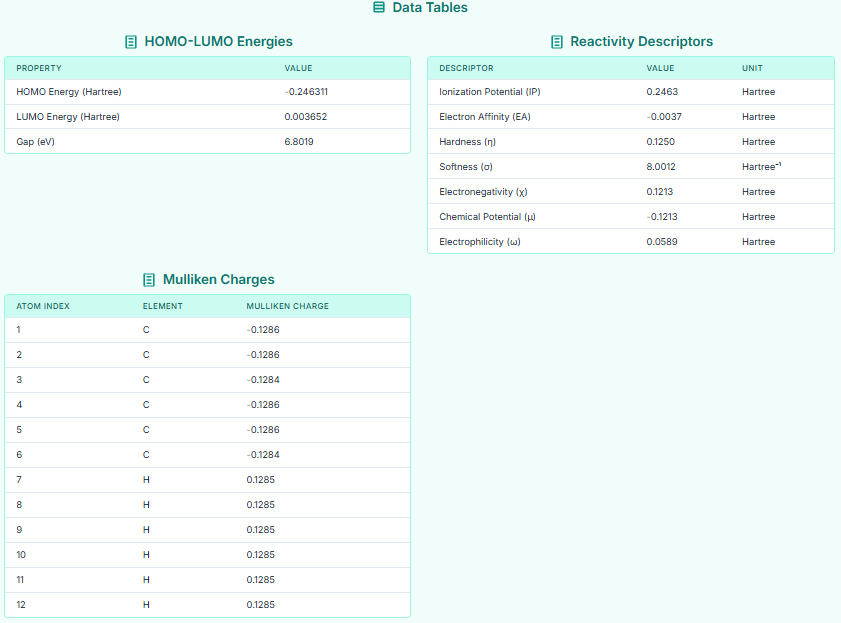
With the DFT tool, the input molecular structure is subjected to a quantum chemical calculation, generating a precise set of electronic properties. These values, including the HOMO-LUMO energy gap, ionization potential, and chemical hardness, provide a detailed profile of the molecule's reactivity, stability, and electron-donating or -accepting capabilities. Therefore, by using the DFT tool to calculate and organize these fundamental descriptors, the in-depth quantum chemical analysis of the compound is completed successfully.
