Introduction to Post-Docking Analysis (PDA)
The Post-Docking Analysis (PDA) tool is a comprehensive and versatile platform designed to critically evaluate and interpret results from multiple molecular docking platforms. By implementing sophisticated algorithms, PDA moves beyond simple scoring functions to conduct a multi-faceted assessment, analyzing important details such as binding pose stability, specific intermolecular interaction patterns and the overall complementarity between a ligand and its binding site.
Its primary strength lies in streamlining the often-cumbersome post-docking workflow, offering automated analysis for large-scale virtual screening campaigns that generate thousands of potential hits. Ultimately, PDA empowers researchers to efficiently sift through vast datasets, filter out false positives, and confidently identify the most promising protein-ligand complexes for progression in a structure-based drug design pipeline.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Execute the Tool
Before fetching your job, you must specify which software was originally used for the docking calculation. From the "Docking Tool" dropdown menu, select the appropriate program (e.g., LigandLock) from the list.
To begin your analysis, enter the unique Job ID from your completed docking run and click "Fetch Job" to load the necessary result files.
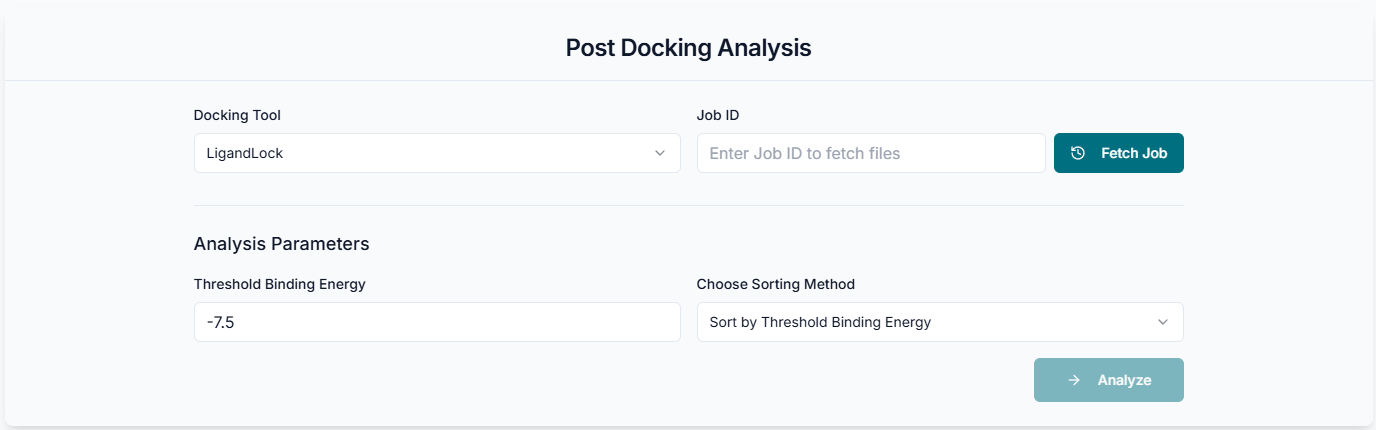
This is the PDA tool's application workspace page, where various options for the comprehensive analysis of molecular docking results are provided.
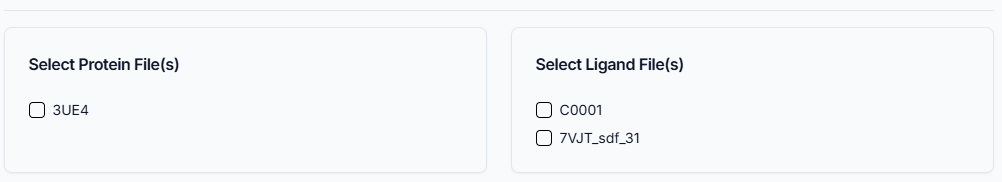
Selecting Protein and Ligand Files
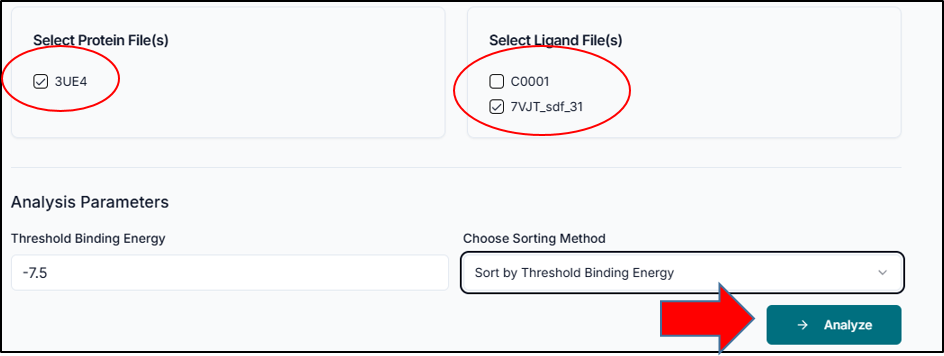
After successfully loading your job, the system displays the protein and ligand files available from your original docking run. To proceed, you must specify which complex you want to analyze. Select the desired protein file (e.g., 3UE4) and the specific ligand file(s) (e.g. C0001 or 7VJT_sdf_31) by clicking the checkbox next to each name. This selection tells the tool which protein-ligand pair(s) to focus on for the subsequent interaction and binding analysis.
Configuring and Running the Analysis
In the "Analysis Parameters" section, you can define the criteria for filtering and sorting your docking results. First, set the "Threshold Binding Energy" to focus on high-affinity poses; for instance, a value of -7.5 will only include results with a binding score of -7.5 kcal/mol or better. Next, use the "Choose Sorting Method" dropdown to organize the output, such as ranking the poses by their binding energy. Once you have configured these parameters for your selected protein and ligand, click the "Analyze" button to run the post-docking analysis.
Viewing and Downloading Results
Upon completion, the "Analysis Results" are presented in a clear, sortable table. Each row corresponds to a ligand from your selection, displaying its Name and the calculated Binding Energy. You can sort the list by clicking the "Binding Energy" header to quickly identify the top-scoring compounds, and for any result of interest, you can click "Download" to save the specific binding pose for further visualization and analysis. Use the pagination controls at the bottom to navigate through all the generated results.
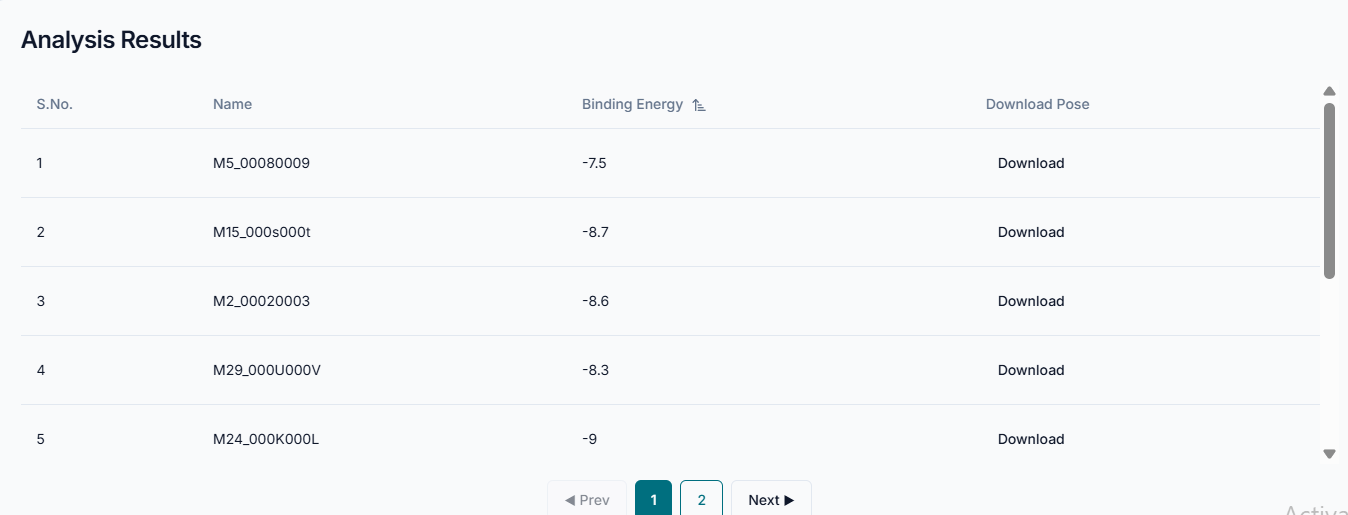
With the PDA tool, the vast set of binding poses from a molecular docking experiment is systematically processed and filtered based on user-defined criteria, such as a binding energy threshold. The tool organizes the poses that meet this threshold into a clear, ranked table where a lower (more negative) binding energy signifies a stronger and more favorable interaction. Therefore, by using the PDA tool to filter a large dataset down to the most potent candidates, the post-docking analysis is completed successfully.
