Introduction to Mutation Inducer
Mutation induction plays an important role in drug discovery by supporting the systematic exploration of how structural changes impact molecular function, particularly in proteins. Mutation Inducer is built around a sequence-based deep learning framework that predicts protein stability changes resulting from point mutations.
At its core, it influences a pretrained protein language model trained on large-scale protein sequence data to capture intricate patterns and contextual relationships within amino acid sequences. This allows the model to assess the effect of specific mutations on protein stability with high accuracy, even in the absence of structural data.
By focusing on single-point mutations, the tool provides detailed visions into which substitutions are likely to enhance or reduce protein stability, which is an essential factor in understanding disease mechanisms, guiding protein engineering and optimizing biologics. The deep learning backbone confirms that the predictions are not only fast but also generalizable across diverse protein families. Researchers can use the tool to prioritize stabilizing mutations, design full-bodied proteins or screen variants for therapeutic development. In the broader context of drug discovery, this capability benefits in refining targets, improving binding interactions and confirming better manufacturability of biologic drugs.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Execute the Tool
Before executing the tool, you must create a Job ID. You can customize this ID or click the "Create Job ID" button to have one generated for you automatically.
TIP: Without creating a JOB ID, you will not be able to access any options of the tool.

This is the Mutation Inducer tool's application workspace page, where various options for analysing sequences and predicting stability changes through targeted point mutations are provided. This tutorial will explain each option in detail.
Predicting Stability Changes Using a FASTA Sequence
From the "Paste FASTA" tab, you will enter the name of the sequence and paste the FASTA sequence without any header.
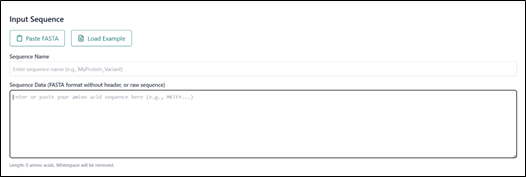
Added the sequence name and pasted the FASTA sequence. For example, here we took the FASTA sequence from PDB ID: 2OCJ, chain A.
Defining and Running the Mutation
To create a mutation, first select the original amino acid from the dropdown, specify the position where the mutation should occur, and then choose the mutated amino acid from the second dropdown. The resulting mutation will be displayed in the preview column. For example, if glutamine (Q) at position 51 is mutated to threonine (T), it will appear as Q51T.
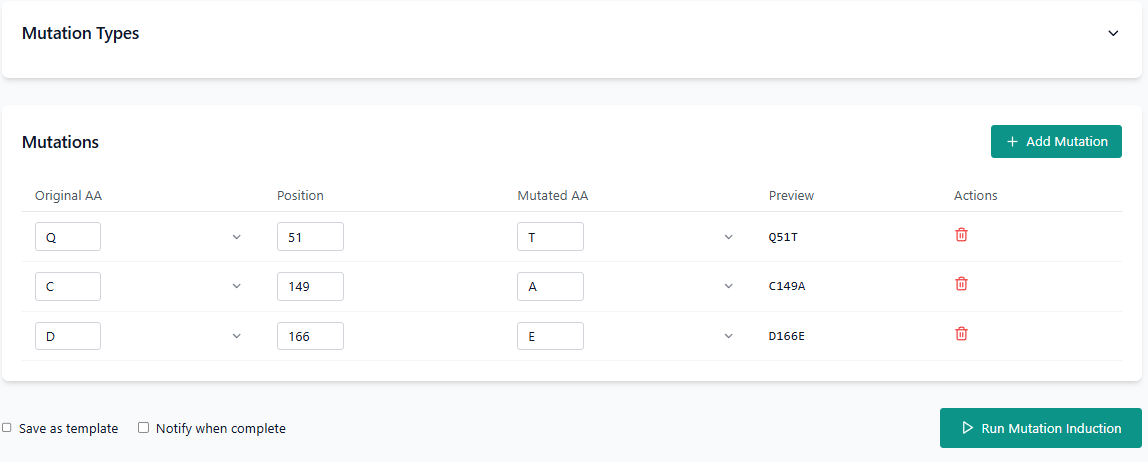
To submit the stability prediction, click on the "Run Mutation Inducer" button.

Analyzing the Results
You can view the results after the job is complete.

In the Mutation Inducer tool, each mutation is assigned a predicted ΔΔG value, which reflects its impact on protein stability. A negative ΔΔG indicates a stabilizing mutation, while a positive ΔΔG indicates a destabilizing effect. So, by using the Mutation Inducer tool, the stability prediction is completed successfully.
